Servo Motor Features Overview
Features of Servo Motors
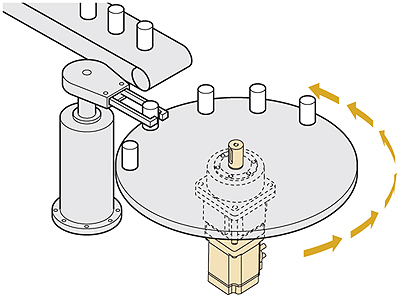
The servo motor is specialized for high-response, high-precision positioning. As a motor capable of accurate rotation angle and speed control, it can be used for a variety of equipment.
Closed Loop Control
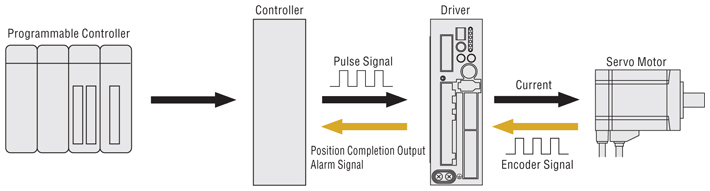
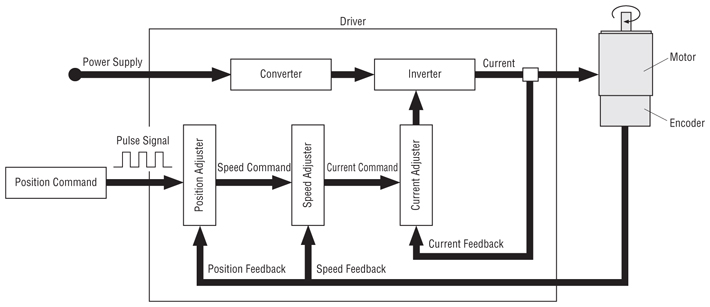
A rotation detector (encoder) is mounted on the motor and feeds the rotation position/speed of the motor shaft back to the driver. The driver calculates the error of the pulse signal or analog voltage (position command/speed command) from the controller and the feedback signal (current position/speed) and controls the motor rotation so the error becomes zero. The closed loop control method is achieved with a driver, motor and encoder, so the motor can carry out highly accurate positioning operations.
- An END signal is obtained that communicates the completion of the positioning operation.
- An alarm can be output if there is an abnormality such as an overload, making it possible to communicate equipment abnormalities.
Position Control Using a Pulse Signal
The controller inputs the pulse signal. The speed and stop position are then controlled according to the pulse number.
Position Control Diagram
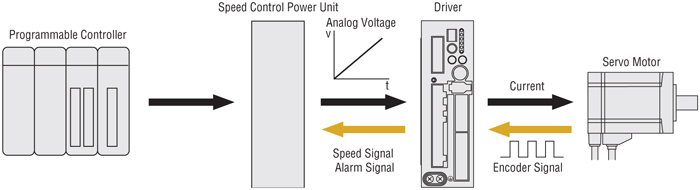
Speed Control by Analog Voltage
The analog voltage is input to control the speed.
Speed Control Diagram
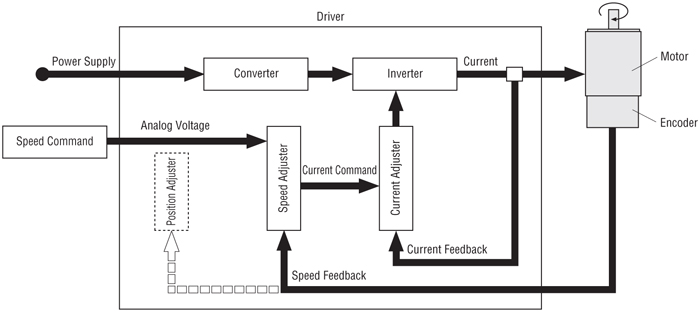
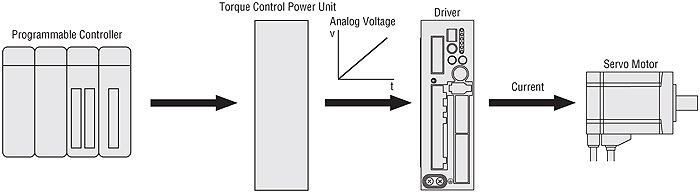
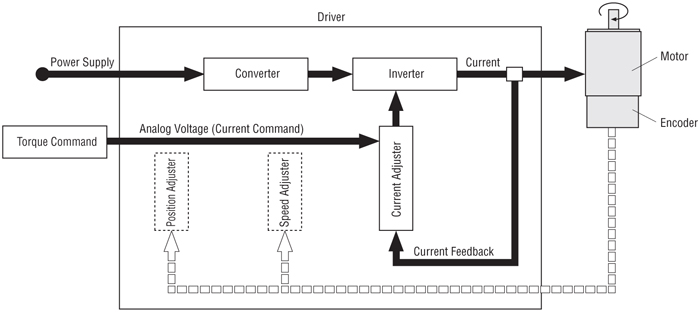
Torque Control by Analog Voltage
The analog voltage is input to control torque.
Torque Control Diagram
Compact and High Power
The servo motor is compact and lightweight and outputs high power.
- Speed-Torque Characteristics
Rated Output Power: 200 W (1/4 HP)
Motor Frame Size: 60mm (2.36 in.)
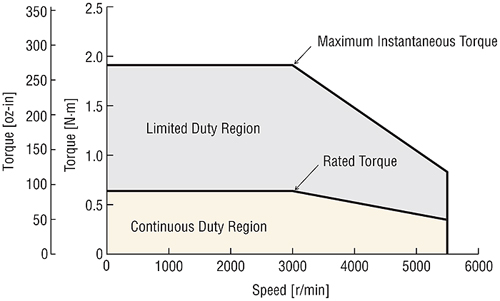
Continuous Duty Region and Limited Duty Region
A servo motor controls the current according to the state of the load. Because of the efficiency and low heat generation of the motor, continuous operation is possible within the rated torque. Also, during acceleration and deceleration, the limited duty region is used to obtain a large torque, making it possible to decrease the positioning time.
A Wide Variable Speed Range
A flat, stable torque is generated from low-to high-speed range, so that long-stroke positioning can be carried out quickly. The machine cycle is improved in testing equipment by quickly returning at high speed after slowly transporting the workpiece at low speed.
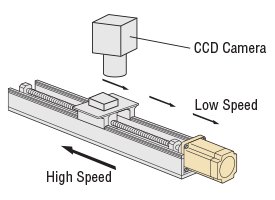
Geared Type also Compatible with Large Inertia Loads
The servo motor has restrictions on the permissible load inertia, but the geared type can be used to greatly increase the load size that can be driven.