Constant Speed AC Motors & Gear Motors
Induction AC Motors & Gear Motors

AC induction motors are optimal for uni-directional and continuous operation such as a conveyor system. All you need is to connect a capacitor and plug the motor into an AC power supply and the motor can be easily operated.
- 1 W (1/750 HP) up to 3 HP
- Parallel Shaft, Right-Angle Solid Shaft or Right-Angle Hollow Shaft Gears, Round Shaft (no Gear) and 2-Pole High-Speed Types
- Electromagnetic Brake Available
- Single-Phase 110/115 or 220/230 VAC, Three-Phase 200/220/230 or 460 VAC
Reversible AC Motors & Gear Motors

Generating a greater starting torque than induction motors and having a built-in friction brake, these single-phase AC motors allow for instantaneous switching of rotation direction.
- 1 W (1/750 HP) up to 90 W (1/8 HP)
- Parallel Shaft, Right-Angle Solid Shaft or Right-Angle Hollow Shaft Gears, Round Shaft (no Gear) Types
- Electromagnetic Brake Available
- Single-Phase 110/115 or 220/230 VAC
Washdown AC Gear Motors

Washdown gear motors are watertight, dust-resistant geared induction motors which conform to the IEC standard IP67 or IP65. They can be used where they are splashed with water.
- 25 W (1/30 HP) up to 3 HP
- Parallel Shaft, Right-Angle Solid Shaft or Right-Angle Hollow Shaft Gears
- IP67 or IP65 Rated
- Single-Phase 110/115 or 220/230 VAC, Three-Phase 200/220/230 or 460 VAC
Torque Motors & Gear Motors

A special rotor is used to provide large starting torque and sloping characteristics (torque is highest at zero speed and decreases steadily with increasing speed). The torque can be changed by changing the applied voltage.
- 3 W (1/250 HP) up to 20 W (1/38 HP)
- Parallel Shaft Gear or Round Shaft (no Gear)
- Single-Phase 110/115 or 220/230 VAC
Low-Speed Synchronous Motors & Gear Motors

Low-speed synchronous motors provide highly precise speed regulation, low-speed rotation and quick bi-directional rotation. The basic construction of low-speed synchronous motors is the same as that of stepper motors.
- 1.65 in. (42 mm) up to 3.54 in. (90 mm)
- Parallel Shaft Gear or Round Shaft (no Gear)
- Single-Phase 100-115 VAC
NEMA 56C Speed Reducers

The gears in these NEMA 56C speed reducers are high strength, maintenance free and can be mounted in any direction with their slip fit "O" ring design. Low to high reduction ratios, flange mount or foot mount types, right angle or hollow shaft right angle types available. Fit NEMA 56C AC motors, brushless DC motors and brushed DC motors.
- 1/2 HP or 1 HP Input Power
- Inline Helical Gear Speed Reducers
- Right-Angle Hypoid Gear Speed Reducers
Features and Types of Constant Speed Motors & Gear Motors
Constant speed motors come in various types as shown below. Select from a wide range of products depending on the application, required functions, output, etc.
Easy Operation
AC motors and gear motors include single-phase motors used with a single-phase AC power supply and three-phase motors used with a three-phase AC power supply. A single-phase motor can be operated by simply connecting it to a single-phase power supply via the supplied capacitor. A three-phase motor does not require a capacitor. All you need is to connect the motor directly to a three-phase AC power supply.
The Power Supply Frequency Determines the Speed
The basic speed (synchronous speed) of a standard AC motor is determined by the power supply frequency and the number of poles. Many of our standard AC motors have four poles, so their synchronous speed is as follows:
- 50 Hz: 1500 r/min
- 60 Hz: 1800 r/min
The actual speed varies according to the load torque.
With our motors, the speed roughly falls within the following ranges at a load torque equivalent to the rated torque:
- 50 Hz: 1200 to 1300 r/min
- 60 Hz: 1450 to 1600 r/min
The rated speed of our standard AC motors are set within the above ranges and shown in each motor's specifications. To calculate a more accurate machine speed, use the rated speed as a reference.
The power supply frequency varies from region to region. In the case of automated equipment used in different regions, change the gear ratio of the gearhead or take the appropriate measure to obtain the desired speed.
Induction Motors
These motors can be easily operated from an AC power supply. Single-phase and three-phase motors are available.
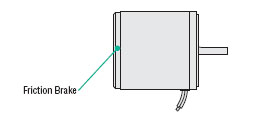
Reversible Motors
Generating a greater starting torque and having a built-in friction brake, these single-phase AC motors allow for instantaneous switching of rotation direction.
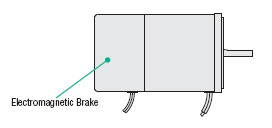
Electromagnetic Brake Type (Induction or Reversible Motor)
These AC motors adopt a power off activated type electromagnetic brake to hold the load in position when the power is cut off.
Washdown Motors
Geared AC motors of excellent watertight, dust-resistant structure. These AC motors conform to the IEC standard IP67 or IP65.
Torque Motors
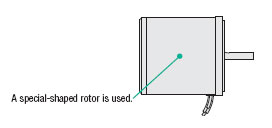
A special rotor is used to provide large starting torque and sloping characteristics (torque is highest at zero speed and decreases steadily with increasing speed). The torque can be changed by changing the applied voltage.
Low-Speed Synchronous Motors
Uses the same stator and rotor as stepping motors. The motor offers superb starting, stopping and reversing characteristics as well as synchronous operation.