Transport Robot Applications

As more and more companies seek to introduce machines to perform simple tasks, efforts to automate and save labor on comparatively simple tasks such as moving goods, are accelerating. One solution to this challenge has been the introduction of transport robots (AGV/AMR/GTP*).
With the ability to run on battery power, our BLV Series R Type and BLH Series brushless motors can be used as the drive axle for transport robots or embedded in other similar transport devices. These motors contribute to the handling of a wide variety of operating patterns and transport modes in various workplace environments.
*AGV: Automatic Guided Vehicle. AMR: Autonomous Mobile Robot. GTP: Goods To Person
Low-Platform and Thin Design
Automating Shelf or Basket-Type Carts
Low-floor transport robots can be used to lift (or "chuck") shelf and basket-type carts, making them effective tools for the automation of transport tasks. Motors may be mounted to the top or side of a robot, allowing for greater freedom in low-floor designs.
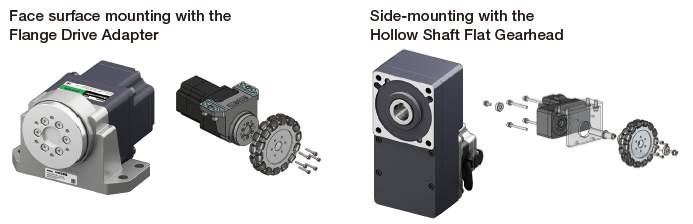
For Passing in Narrow Spaces
The use of opposing hollow shaft flat gearheads reduces the distance between the wheels, allowing for a slim design that reduces the width of the device. This makes it possible to have multiple devices pass each other in narrow spaces, contributing to reduced transport robot wait times and increased operation rates.
Improved Design
Compact, Lightweight Driver
Thanks to their compact size, these drivers allow for improved freedom of layout for the location of batteries and control devices.
Electric Brake*
The use of electric brakes to maintain stop positions makes mechanical (i.e. electromagnetic) brakes unnecessary. The reduction of the total length of the motor allows narrower device designs.
*Effective only when power is ON
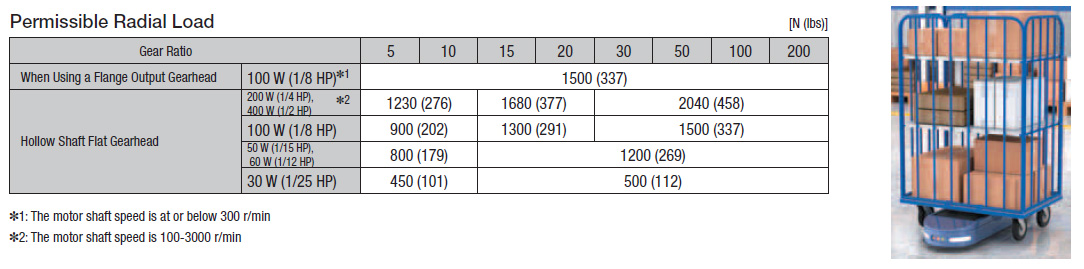
High Power
For Larger Loads and Use in Robots and Conveyors
A transport robot’s load capacity is affected by its permissible radial load. When using a Flange Drive Adapter, it is 1500 N (153 kgf) [337 lbs (742 lbf)]. When using a hollow shaft flat gearhead, it reaches a maximum strength of 2040 N (208 kgf) [458 lb (1009 lbf)]. This supports such the requirements of increasing load size and installation in robots and conveyors.
Stop Position Setting & Fine Adjustment
Setting the Remaining Distance from a Specified Position
With the ability to set travel distance, it is not only possible to travel a present distance on a guide, but also to perform partial positioning operations, such as setting the distance from the sensor input position to the target stop position during automated operation.

Fine-tuning Stop Positions
Motor shaft speed can be set from 1 r/min. Based on a wheel diameter of 100 mm (3.34 in.), this results in a transport speed of approximately 0.3 m/min (11.8 in/min). Such extremely slow speeds reduce the risk of overrun and allow for minute adjustment of stop positions.
Fix Devices in Place to Stabilize Transport Tasks
The incorporation of both mechanical (i.e. electromagnetic) and electric brakes makes it possible to fix devices in place when they are stopped. This helps to maintain devices in position when transporting goods on flat or sloped ground, and can improve the stability of tasks.


Straight Travel, Evasion and Stopping

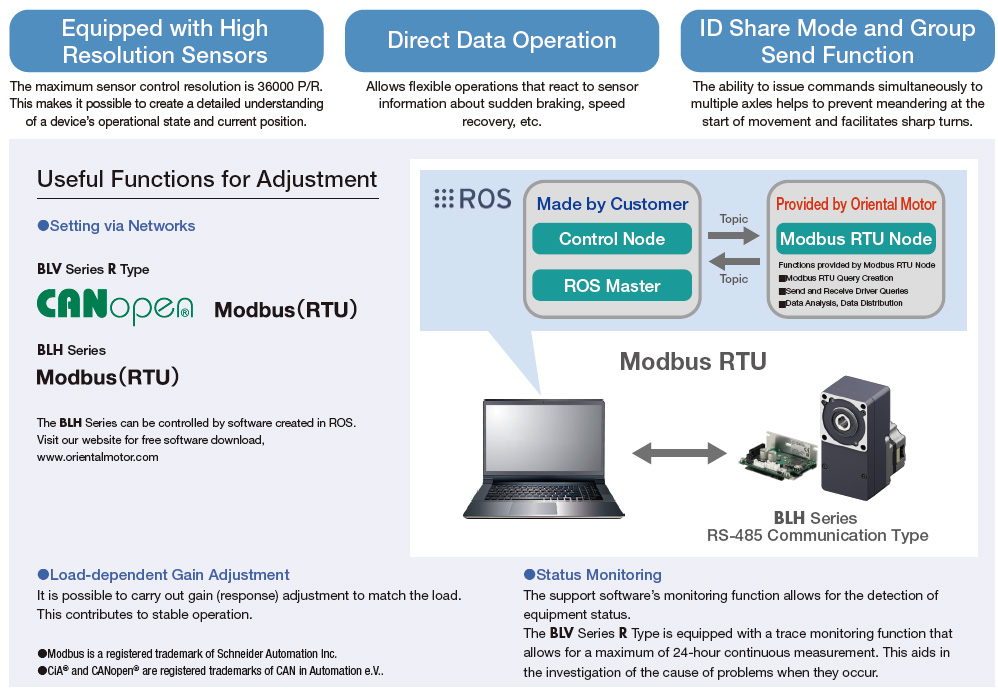
Transport robots must exhibit high-performance movement that considers various factors, such as different floor conditions and the need to quickly maneuverer around obstacles. The ability to send feedback signals from the motor and issue commands to each shaft allows for the flexible adjustment of straight travel, evasion and stopping operations.
Transport Robot Compatible Products
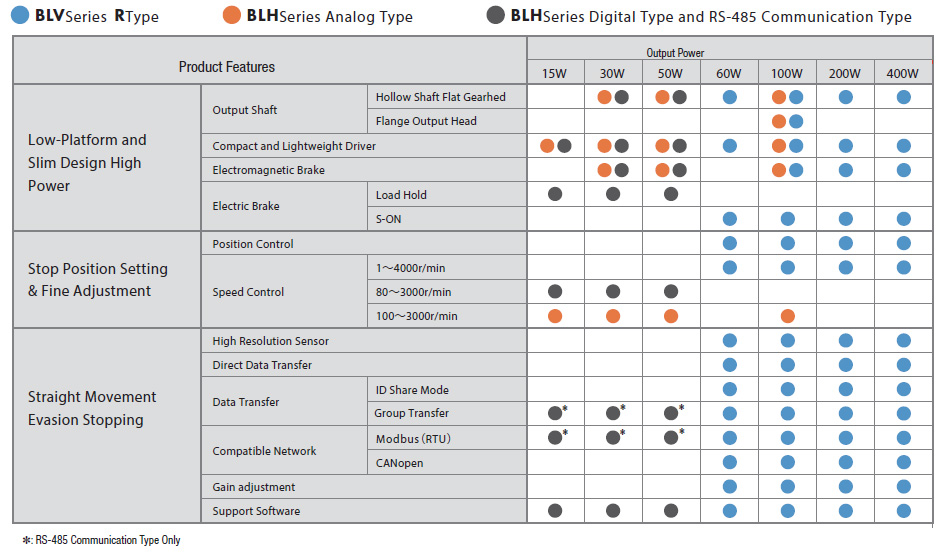
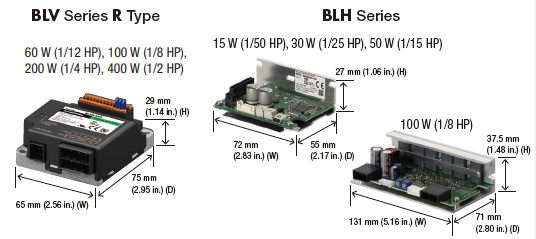
BLV Series R-Type
The BLV Series is a selection of brushless DC motors which have been made more compact and lightweight. The ability to operate on battery power supports the development of more compact devices. The BLV Series supports Modbus (RTU) and CANopen communication protocols.
- Output Power: 60 W (1/12 HP), 100 W (1/8 HP), 200 W (1/4 HP), 400 W (1/2 HP)
- DC Voltage range: 24-48 VDC
- Output Shaft Type: Parallel shaft gearhead, hollow shaft flat gearhead, round shaft
- Electromagnetic Brake Available
BLH Series
The BLH Series is equipped with a compact 24 VDC board-type driver, and is available in three driver types: Analog, Digital and RS-485 Communication.
- Output Power: 15 W (1/50 HP), 30 W (1/25 HP), 50 W (1/15 HP), 100 W (1/1/8 HP)
- DC Voltage range: 24 VDC
- Parallel shaft gearhead, CS gearhead, hollow shaft flat gearhead, round shaft
- Electromagnetic Brake Available
Resources